Introduction
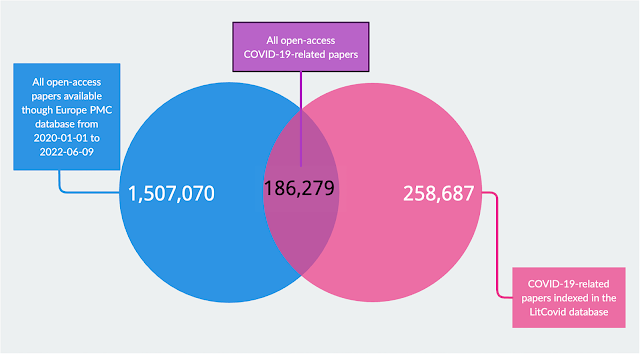
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance of reliable health advice, leading to increased scrutiny on the transparency of research practices. Transparent scientific practices not only foster trust but also play a vital role in combating misinformation. In our recent study by Ahmad Sofi-Mahmudi, Eero Raittio, we assessed adherence to five transparency practices in open-access COVID-19 research articles.
Aim
Assessing Transparency Practices in COVID-19 Research: The study aimed to evaluate five key transparency practices in COVID-19 research articles: data availability, code availability, protocol registration, conflicts of interest (COI) disclosure, and funding disclosures.Results
The findings revealed both encouraging and concerning trends among the analyzed research articles:
✅ Conflicts of Interest (COI) Disclosure: Over 90% of the articles disclosed potential conflicts of interest, which is a positive sign for research integrity and transparency.
✅ Funding Disclosure: Funding disclosure was common in randomized controlled trials (RCTs), with 83.9% of articles providing this information. However, funding disclosures were less frequent in reviews and research articles, indicating the need for increased transparency in these areas.
✅ Protocol Registration: Protocol registration was more prevalent in RCTs, with 53.5% of articles adhering to this practice. However, there is room for improvement in encouraging protocol registration in reviews and research articles to enhance research reproducibility.
❌ Data Sharing: Shockingly, only 2.5% of articles shared their data openly, indicating a significant lack of transparency in this critical aspect of research.
❌ Code Sharing: Code sharing was even rarer, with only 0.4% of articles providing access to their code. This hampers the reproducibility of studies and inhibits collaboration among researchers.
✅ Conflicts of Interest (COI) Disclosure: Over 90% of the articles disclosed potential conflicts of interest, which is a positive sign for research integrity and transparency.
✅ Funding Disclosure: Funding disclosure was common in randomized controlled trials (RCTs), with 83.9% of articles providing this information. However, funding disclosures were less frequent in reviews and research articles, indicating the need for increased transparency in these areas.
✅ Protocol Registration: Protocol registration was more prevalent in RCTs, with 53.5% of articles adhering to this practice. However, there is room for improvement in encouraging protocol registration in reviews and research articles to enhance research reproducibility.
❌ Data Sharing: Shockingly, only 2.5% of articles shared their data openly, indicating a significant lack of transparency in this critical aspect of research.
❌ Code Sharing: Code sharing was even rarer, with only 0.4% of articles providing access to their code. This hampers the reproducibility of studies and inhibits collaboration among researchers.
Conclusion
In this era of rapidly evolving information and uncertainty, transparency is paramount to ensure the credibility of health advice. Our study highlights the need for researchers and scientific journals to embrace open science practices fully. By enhancing transparency in COVID-19 research, we can foster public trust and strengthen the fight against the pandemic.
Research and Clinical Implications
Our results emphasize the need for a stronger commitment to open science in COVID-19 research. While COI disclosure was widespread, other essential transparency practices, such as data and code sharing, were severely lacking.
Transparent scientific practices have profound implications for building public trust and fostering collaboration. By openly sharing data, methods, and results, researchers can ensure the credibility of their findings and contribute to the global efforts against the pandemic and infodemic.
Read the full research article here: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0288406
Read the full research article here: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0288406
Transparency of COVID-19-related research: A meta-research study
Ahmad Sofi-Mahmudi, Eero Raittio, Sergio E. Uribe


Comments
Post a Comment